CVT Basics
Unlike traditional automatic transmissions, continuously variable transmissions don't have a gearbox with a set number of gears, which means they don't have interlocking toothed wheels. The most common type of CVT operates on an ingenious pulley system that allows an infinite variability between highest and lowest gears with no discrete steps or shifts.
Unlike traditional automatic transmissions, continuously variable transmissions don't have a gearbox with a set number of gears, which means they don't have interlocking toothed wheels. The most common type of CVT operates on an ingenious pulley system that allows an infinite variability between highest and lowest gears with no discrete steps or shifts.

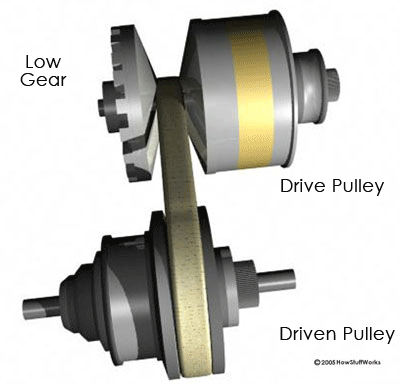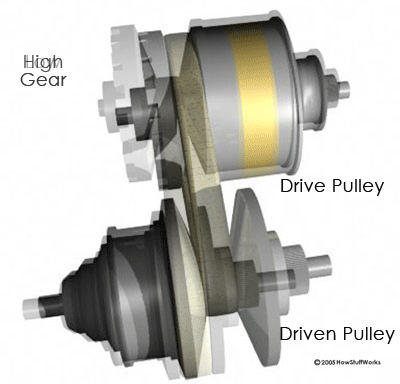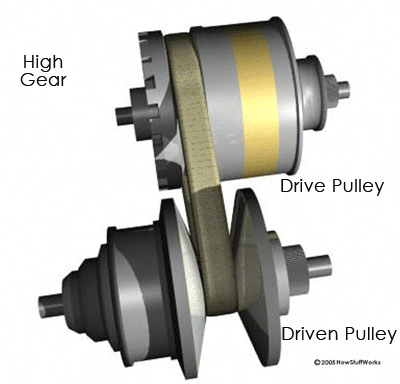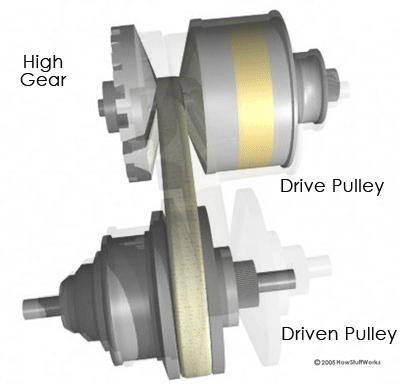
The variable-diameter pulleys are the heart
of a CVT. Each pulley is made of two 20-degree cones facing each other. A belt
rides in the groove between the two cones. V-belts are preferred if the belt is made of
rubber. V-belts get their name from the fact that the belts bear a V-shaped
cross section, which increases the frictional grip of the belt.
When the two
cones of the pulley are far apart (when the diameter increases), the belt rides
lower in the groove, and the radius of the belt loop going around the pulley
gets smaller. When the cones are close together (when the diameter decreases),
the belt rides higher in the groove, and the radius of the belt loop going
around the pulley gets larger. CVTs may use hydraulic pressure, centrifugal
force or spring tension to create the force necessary to adjust the pulley
halves.
Variable-diameter
pulleys must always come in pairs. One of the pulleys, known as the drive pulley (or driving pulley), is connected to the crankshaft of the engine. The
driving pulley is also called the input pulley because it's where the energy from the
engine enters the transmission. The second pulley is called the driven pulley because
the first pulley is turning it. As an output pulley, the driven pulley
transfers energy to the driveshaft.
The distance between the center of the pulleys to where the belt makes
contact in the groove is known as the pitch radius. When the pulleys are far
apart, the belt rides lower and the pitch radius decreases. When the pulleys
are close together, the belt rides higher and the pitch radius increases. The
ratio of the pitch radius on the driving pulley to the pitch radius on the
driven pulley determines the gear.
When one pulley increases its radius, the
other decreases its radius to keep the belt tight. As the two pulleys change
their radii relative to one another, they create an infinite number of gear
ratios -- from low to high and everything in between. For example, when the
pitch radius is small on the driving pulley and large on the driven pulley, then
the rotational speed of the driven pulley decreases, resulting in a lower
“gear.” When the pitch radius is large on the driving pulley and small on the
driven pulley, then the rotational speed of the driven pulley increases,
resulting in a higher “gear.” Thus, in theory, a CVT has an infinite number of
"gears" that it can run through at any time, at any engine or vehicle
speed.
CVT Benefits
Continuously variable transmissions
are becoming more popular for good reason. They boast several advantages that
make them appealing both to drivers and to environmentalists. The table below
describes some of the key features and benefits of CVTs.
Advantages of CVTs
|
|
Feature
|
Benefit
|
Constant,
stepless acceleration from a complete stop to cruising speed
|
Eliminates
"shift shock" -- makes for a smoother ride
|
Works to keep
the car in its optimum power range regardless of how fast the car is
traveling
|
Improved fuel
efficiency
|
Responds
better to changing conditions, such as changes in throttle and speed
|
Eliminates
gear hunting as a car decelerates, especially going up a hill
|
Less power
loss in a CVT than a typical automatic transmission
|
Better
acceleration
|
Better
control of a gasoline engine's speed range
|
Better
control over emissions
|
Can
incorporate automated versions of mechanical clutches
|
Replace
inefficient fluid torque converters
|